欢迎大家赞助一杯啤酒🍺 我们准备了下酒菜:Formal mathematics/Isabelle/ML, Formal verification/Coq/ACL2, C++/F#/Lisp
量子计算
小 (→链接) |
小 (→书籍) |
||
| (未显示1个用户的56个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
{{SeeWikipedia|Quantum computing}} | {{SeeWikipedia|Quantum computing}} | ||
| − | Quantum | + | Quantum computing、量子计算、量子计算机、Quantum information、量子信息 |
==简介== | ==简介== | ||
| + | 1981年,诺贝尔物理学奖获得者理查德-费曼发表了他的开创性演讲 "用计算机模拟物理(Simulating Physics with Computers)"。他的想法是,与经典计算机只能近似地模拟物理学不同,量子计算机可以精确地模拟(simulate it exactly)物理学--如量子物理学(quantum physics)。在1982年发表的一篇论文中,他说:"因此,我相信这是真的,用一类合适的量子机(suitable class of quantum machines),你可以模仿任何量子系统,包括物理世界。" | ||
| + | |||
量子计算的概念最早是 1982 年由美国物理学家费曼提出的,费曼认为:“遵循量子力学法则的量子计算机可能是模拟现实世界量子系统的最好方式”。 | 量子计算的概念最早是 1982 年由美国物理学家费曼提出的,费曼认为:“遵循量子力学法则的量子计算机可能是模拟现实世界量子系统的最好方式”。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1982年,费曼指出,在传统的图灵机上似乎无法高效地模拟量子力学,并建议建立量子计算机来执行这种模拟。 | ||
量子计算机本质上是一个量子力学系统。 | 量子计算机本质上是一个量子力学系统。 | ||
| + | |||
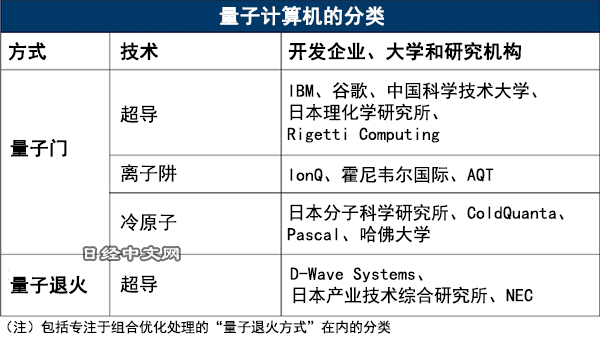
| + | [[文件:quantum-computing-type.jpg]] | ||
==新闻== | ==新闻== | ||
| + | *[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nZu5hutqANk IBM Quantum State of the Union 2022] 433 个量子位(qubits)IBM Osprey 处理器问世 (2022/11/15) | ||
| + | *[https://cn.nikkei.com/industry/scienceatechnology/49608-2022-08-29-08-26-17.html 量子计算机有第3种方式,日本走在前列] 研发团队利用这个实验装置实现了400个量子位,大幅超过现有量子计算机上实现的量子位数量。大森贤治教授表示,“到1~2年后将轻松增至1000个量子位。从原理上讲可增至1万个量子位”。(2022/08/29) | ||
*[https://research.ibm.com/blog/127-qubit-quantum-processor-eagle IBM Quantum breaks the 100‑qubit processor barrier] IBM 量子公司突破 100 量子比特大关 | *[https://research.ibm.com/blog/127-qubit-quantum-processor-eagle IBM Quantum breaks the 100‑qubit processor barrier] IBM 量子公司突破 100 量子比特大关 | ||
| − | == | + | ==指南== |
| + | *[https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/azure/quantum/ Azure Quantum 文档] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==理论== | ||
| + | 实现量子计算本质是利用量子相干性(quantum coherence),不过测量操作会影响量子相干性,使之出现坍缩现象,即所谓的退相干(decoherence)。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==形式语义== | ||
| + | 陆汝钤《计算系统的形式语义》中的量子语言的形式语义,量子语言多基于冯·诺伊曼(von neumann)建立的量子力学的公理体系。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 而这个公理体系又是建立在希尔伯特空间(Hilbert space)的概念之上的。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==量子模拟== | ||
| + | 量子模拟就是利用人为控制的量子系统去模仿实际的物理系统。目前对量子模拟的研究主要集中在光学晶格束缚冷原子系统。一方面,由于激光的可控性,人们可以制备各种维度、各种结构和形状的光晶格;令一方面,由于冷原子可以是玻色子、费米子,或者它们的混合,同时可以通过 Feshbach 共振技术来调节被束缚粒子的等效相互作用强度,因此可以利用晶格中的冷原子系统模拟许许多多复杂的凝聚态物理和高能物理系统,如:费米原子的高温超流,无序 Bose 晶格气体,偶极子的超流和晶格测量领域。《凝聚态物理学》下册 p.708,冯端 | ||
==项目== | ==项目== | ||
| + | [[文件:quil-language-logo.png|right|Quil language]] | ||
| + | [[文件:qosf-logo.png|right|Quantum Open Source Foundation]] | ||
| + | *[https://awesomeopensource.com/projects/quantum Quantum Open Source Projects] @ Awesome Open Source | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/qosf/awesome-quantum-software Open-Source Quantum Software Projects] | ||
| + | *[https://qosf.org/ Quantum Open Source Foundation] [https://www.qosf.org/project_list/ List of Open Quantum Projects] | ||
*[https://github.com/topics/quantum-computing Quantum Computing GitHub Topic] | *[https://github.com/topics/quantum-computing Quantum Computing GitHub Topic] | ||
| + | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_programming Quantum programming] | ||
| + | *[https://www.mathstat.dal.ca/~selinger/quipper/ Quipper: A Scalable Quantum Programming Language] Made by [[Haskell]] | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/inQWIRE/QWIRE QWIRE] a [[Coq]] implementation of the QWIRE quantum programming language | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/quil-lang Quil] quantum programming language and ecosystem. [[Common Lisp]] 编写 | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/quil-lang/qvm qvm: A High-Performance Quantum Virtual Machine] for Quil. [[Common Lisp]] 编写 | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/rigetti/pyquil PyQuil] is a Python library for quantum programming using Quil | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/dwavesystems D-Wave Systems @ GitHub] | ||
*[https://github.com/microsoft/qsharp-compiler Q# Compiler] [https://github.com/microsoft/qsharp-runtime Q# runtime] | *[https://github.com/microsoft/qsharp-compiler Q# Compiler] [https://github.com/microsoft/qsharp-runtime Q# runtime] | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/eth-sri/silq Silq] | ||
| + | *[https://qiskit.org/ Qiskit] | ||
| + | *[https://quantumai.google/cirq Cirq] | ||
*[https://github.com/microsoft/QuantumKatas Quantum Katas] | *[https://github.com/microsoft/QuantumKatas Quantum Katas] | ||
*[https://github.com/quantumlib quantumlib] | *[https://github.com/quantumlib quantumlib] | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/OpenJij/OpenJij OpenJij] Framework for the Ising model and QUBO. [https://www.dwavesys.com/media/xbmotcjg/23_jij_qubits2019-3.pdf OpenJij An open-source project towards a unified annealing platform] | ||
| + | *[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6301779/ Open source software in quantum computing] | ||
| + | *[https://openqasm.com/ OpenQASM] is an imperative programming language for describing quantum circuits, written in [[Python]], The file qasm3.g4 is the reference grammar, written in [[ANTLR]]. | ||
| + | *[https://github.com/epiqc/ScaffCC ScaffCC] | ||
| + | *[https://projectq.ch/ ProjectQ] Powerful open source software for quantum computing | ||
| + | *[https://zxcalculus.com/ ZX-calculus] is a graphical language that goes beyond circuit diagrams. | ||
==实现== | ==实现== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==应用== | ||
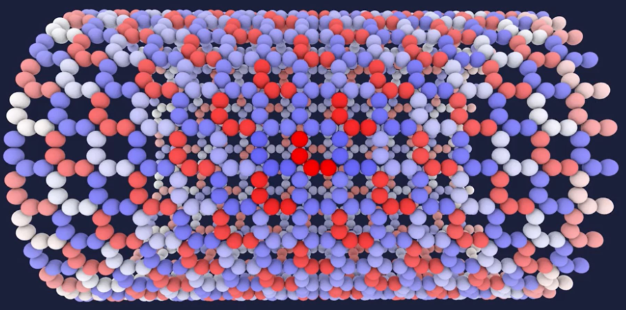
| + | *今天,量子材料模拟(quantum materials simulation)正在被世界各地的科学家积极追求,一些人认为它是量子计算机的第一个 "杀手级应用(killer application)"。 | ||
| + | *[https://www.dwavesys.com/learn/featured-applications D-Wave 250+ Early Quantum Applications] | ||
| + | *[https://www.dwavesys.com/media/hrgpcn5o/qubits-day-2-morning-2-recruit_bah.pdf Display Advertising Optimization] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[文件:quantum-materials-simulation.png]] [https://dwavefederal.com/applications/ 量子材料仿真] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==文档== | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.tulane.edu/quantum/slides/PR18/simcount.pdf Toward the first quantum simulation with quantum speedup] | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.tulane.edu/quantum/slides/PR18/bert.pdf Recursion in circuit description languages] | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.tulane.edu/quantum/slides/PR18/MURI_QPL.pdf Toward Automatic Verification of Quantum Programs] | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.tulane.edu/quantum/slides/PR18/MURIFinal.pptx Continuous Symmetries and Approximate Quantum Error Correction] | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.tulane.edu/quantum/slides/PR18/talk.pdf Adventures in Impredictive Semantics] | ||
| + | *[https://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/people/aleks.kissinger/theses/koch-thesis.pdf Quantum Machine Learning using the ZXW-Calculus] | ||
| + | *[https://www.lanl.gov/projects/national-security-education-center/information-science-technology/dwave/rapid-response-2016.php FY16 D-Wave First Round] [https://www.lanl.gov/projects/national-security-education-center/information-science-technology/dwave/rapid-response-2017.php FY17 D-Wave Second Round] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==书籍== | ||
| + | *《Quantum Computation and Quantum Information》Michael A. Nielsen, Isaac L. Chuang 中文版 清华大学出版社 | ||
| + | *《量子计算机研究 上、下》李承祖 | ||
| + | *《Quantum Computing with Silq Programming: Get up and running with the new high-level programming language for quantum computing》Packt Publishing, 1, 2021, Srinjoy Ganguly, Thomas Cambier | ||
==图集== | ==图集== | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | image:quantum-simulation.png|量子仿真 | ||
| + | image:d-wave.jpeg|D-Wave | ||
| + | image:D-Wave-2000Q.png|D-Wave | ||
| + | image:D-Wave-Quantum-Computer.jpg|D-Wave | ||
| + | image:D-Wave-Ocean.png|D-Wave Ocean | ||
| + | image:quantum-computing-2001-2020.jpg|专利申请和研究投资 | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==链接== | ==链接== | ||
| − | *[https://www.dwavesys.com/ D-Wave Systems] The Practical Quantum Computing Company | + | *[https://www.dwavesys.com/ D-Wave Systems] The Practical Quantum Computing Company [https://dwavefederal.com/ D-Wave for Government] |
| − | *[https://www | + | *[https://www.ibm.com/quantum IBM Quantum Computing] |
*[https://quantumai.google/ Google Quantum AI] | *[https://quantumai.google/ Google Quantum AI] | ||
| + | *[https://www.fujitsu.com/global/services/business-services/digital-annealer/ Fujitsu] 量子科技 - 數位退火技術Digital Annealer | ||
| + | *[https://www.zhinst.com/japan/en 苏黎世仪器 Zurich Instruments] | ||
*[https://www.qtumist.com/ 量子客] | *[https://www.qtumist.com/ 量子客] | ||
[[category:量子计算]] | [[category:量子计算]] | ||
| + | [[category:computer science]] | ||
[[category:mathematics]] | [[category:mathematics]] | ||
[[category:physics]] | [[category:physics]] | ||
| + | [[category:science]] | ||
| + | [[category:Huihoo Foundation]] | ||
2023年5月3日 (三) 09:39的最后版本
| |
您可以在Wikipedia上了解到此条目的英文信息 量子计算 Thanks, Wikipedia. |
Quantum computing、量子计算、量子计算机、Quantum information、量子信息
目录 |
[编辑] 简介
1981年,诺贝尔物理学奖获得者理查德-费曼发表了他的开创性演讲 "用计算机模拟物理(Simulating Physics with Computers)"。他的想法是,与经典计算机只能近似地模拟物理学不同,量子计算机可以精确地模拟(simulate it exactly)物理学--如量子物理学(quantum physics)。在1982年发表的一篇论文中,他说:"因此,我相信这是真的,用一类合适的量子机(suitable class of quantum machines),你可以模仿任何量子系统,包括物理世界。"
量子计算的概念最早是 1982 年由美国物理学家费曼提出的,费曼认为:“遵循量子力学法则的量子计算机可能是模拟现实世界量子系统的最好方式”。
1982年,费曼指出,在传统的图灵机上似乎无法高效地模拟量子力学,并建议建立量子计算机来执行这种模拟。
量子计算机本质上是一个量子力学系统。
[编辑] 新闻
- IBM Quantum State of the Union 2022 433 个量子位(qubits)IBM Osprey 处理器问世 (2022/11/15)
- 量子计算机有第3种方式,日本走在前列 研发团队利用这个实验装置实现了400个量子位,大幅超过现有量子计算机上实现的量子位数量。大森贤治教授表示,“到1~2年后将轻松增至1000个量子位。从原理上讲可增至1万个量子位”。(2022/08/29)
- IBM Quantum breaks the 100‑qubit processor barrier IBM 量子公司突破 100 量子比特大关
[编辑] 指南
[编辑] 理论
实现量子计算本质是利用量子相干性(quantum coherence),不过测量操作会影响量子相干性,使之出现坍缩现象,即所谓的退相干(decoherence)。
[编辑] 形式语义
陆汝钤《计算系统的形式语义》中的量子语言的形式语义,量子语言多基于冯·诺伊曼(von neumann)建立的量子力学的公理体系。
而这个公理体系又是建立在希尔伯特空间(Hilbert space)的概念之上的。
[编辑] 量子模拟
量子模拟就是利用人为控制的量子系统去模仿实际的物理系统。目前对量子模拟的研究主要集中在光学晶格束缚冷原子系统。一方面,由于激光的可控性,人们可以制备各种维度、各种结构和形状的光晶格;令一方面,由于冷原子可以是玻色子、费米子,或者它们的混合,同时可以通过 Feshbach 共振技术来调节被束缚粒子的等效相互作用强度,因此可以利用晶格中的冷原子系统模拟许许多多复杂的凝聚态物理和高能物理系统,如:费米原子的高温超流,无序 Bose 晶格气体,偶极子的超流和晶格测量领域。《凝聚态物理学》下册 p.708,冯端
[编辑] 项目
- Quantum Open Source Projects @ Awesome Open Source
- Open-Source Quantum Software Projects
- Quantum Open Source Foundation List of Open Quantum Projects
- Quantum Computing GitHub Topic
- Quantum programming
- Quipper: A Scalable Quantum Programming Language Made by Haskell
- QWIRE a Coq implementation of the QWIRE quantum programming language
- Quil quantum programming language and ecosystem. Common Lisp 编写
- qvm: A High-Performance Quantum Virtual Machine for Quil. Common Lisp 编写
- PyQuil is a Python library for quantum programming using Quil
- D-Wave Systems @ GitHub
- Q# Compiler Q# runtime
- Silq
- Qiskit
- Cirq
- Quantum Katas
- quantumlib
- OpenJij Framework for the Ising model and QUBO. OpenJij An open-source project towards a unified annealing platform
- Open source software in quantum computing
- OpenQASM is an imperative programming language for describing quantum circuits, written in Python, The file qasm3.g4 is the reference grammar, written in ANTLR.
- ScaffCC
- ProjectQ Powerful open source software for quantum computing
- ZX-calculus is a graphical language that goes beyond circuit diagrams.
[编辑] 实现
[编辑] 应用
- 今天,量子材料模拟(quantum materials simulation)正在被世界各地的科学家积极追求,一些人认为它是量子计算机的第一个 "杀手级应用(killer application)"。
- D-Wave 250+ Early Quantum Applications
- Display Advertising Optimization
[编辑] 文档
- Toward the first quantum simulation with quantum speedup
- Recursion in circuit description languages
- Toward Automatic Verification of Quantum Programs
- Continuous Symmetries and Approximate Quantum Error Correction
- Adventures in Impredictive Semantics
- Quantum Machine Learning using the ZXW-Calculus
- FY16 D-Wave First Round FY17 D-Wave Second Round
[编辑] 书籍
- 《Quantum Computation and Quantum Information》Michael A. Nielsen, Isaac L. Chuang 中文版 清华大学出版社
- 《量子计算机研究 上、下》李承祖
- 《Quantum Computing with Silq Programming: Get up and running with the new high-level programming language for quantum computing》Packt Publishing, 1, 2021, Srinjoy Ganguly, Thomas Cambier
[编辑] 图集
[编辑] 链接
- D-Wave Systems The Practical Quantum Computing Company D-Wave for Government
- IBM Quantum Computing
- Google Quantum AI
- Fujitsu 量子科技 - 數位退火技術Digital Annealer
- 苏黎世仪器 Zurich Instruments
- 量子客