欢迎大家赞助一杯啤酒🍺 我们准备了下酒菜:Formal mathematics/Isabelle/ML, Formal verification/Coq/ACL2/Agda, C++/Lisp/Haskell
JSLEE
2010年9月19日 (日) 15:43的版本
JAIN SLEE is primarily designed to support the rapid development of robust telecommunications applications in Java.
目录 |
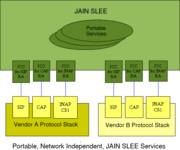
JAIN SLEE and JCC
Using JCC for Portable, Network Independent JAIN SLEE Services
The JAIN Java Call Control (JCC) is an implementation standard for call control in Java. With the related protocol Java Coordinations and Transactions (JCAT) it provides all the capabilites required for the creation of common AIN services, converged voice/data and next generation services. JCC/JCAT is related to Parlay. The call state model used by JCC is the same as Parlay. However, the architecture presented in this document is a service oriented architecture and does not use Parlay's gateway model. The spec lead for JCC, Jean-Luc Bakker, is also the spec lead for Parlay MPCCS.
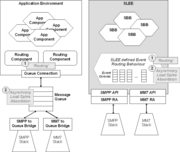
JAIN SLEE for messaging
A simple high level view of a JAIN SEE based messaging application architecture is given in Figure 1. On the left hand side is the common approach taken to build messaging applications that uses a combination of a message queue and an application environment (for example J2EE) that is synchronous in nature. The right hand side shows a JAIN SLEE based architecture.
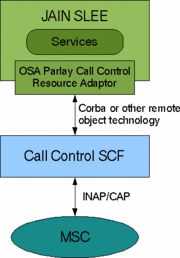
JAIN SLEE and OSA Parlay
JAIN SLEE provides the application environment for OSA/Parlay applications. The OSA/Parlay gateway and SCFs are Resources from the JAIN SLEE perspective. The JAIN SLEE has Resource Adaptors installed that present an API to the application running in JAIN SLEE. This API then talks via a protocol to the gateway and SCF implementation. The OSA/Parlay implementation provides network integration.
OSA/Parlay does not define an application environment and JAIN SLEE does. JAIN SLEE does not define network connectivity and OSA/Parlay does. Therefore they are not competing technologies and in fact both are enhanced by the other.