欢迎大家赞助一杯啤酒🍺 我们准备了下酒菜:Formal mathematics/Isabelle/ML, Formal verification/Coq/ACL2/Agda, C++/Lisp/Haskell
Formal verification
| |
您可以在Wikipedia上了解到此条目的英文信息 Formal verification Thanks, Wikipedia. |
Formal verification
目录 |
简介
“在科学的问题上,一千人的权威比不上一个人谦卑的推理。” ——伽利略
Formal verification, Proof assistant, Theorem Prover, Software verification, Hardware verification ...
形式化方法是一种特别的基于数学的技术,用于软件和硬件系统的形式规范、开发以及验证。
形式验证的含义是根据某个或某些形式规范或属性,使用数学的方法证明其正确性或非正确性。
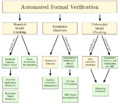
形式验证可以分为三大类:抽象解释(Abstract Interpretation)、形式模型检查(Formal Model Checking,也被称作特性检查)和定理证明(Theory Prover)。
自动化定理证明(Automated theorem proving,ATP)目前是自动推理(Automated reasoning,AR)体系中发展最好的部分,它的目的是为使用电子计算机程序来进行数学定理的证明。对于不同的公理系统,它能够推论出一个定理在此系统下是正确的,还是不可证明的,或者错误的。
这里指包含 Proof assistant 证明助理(证明助手) 在内的所有形式化相关主题,包含计算机辅助定理证明、Coq 证明助理、函数式编程、操作语义、用于论证软件的逻辑和技术、静态类型系统、基于性质的随机测试、以及对实践中编程代码的验证等。
机器证明
笛卡尔曾有过一个宏伟的设想:”一切问题化为数学问题,一切数学问题化为代数问题,一切代数问题化为代数方程求解问题。“他把问题问题想得过于简单了。如果他的设想真能实现,那就不仅是数学的机械化,而且是全部科学的机械化。因为,代数求解是可以机械化的。但笛卡尔没有停留在空想,他所创立的解析几何,在空间形式和数量关系之间架起了一座划时代的桥梁,实现了初等几何问题代数化。这为后来的几何定理机器证明的代数方法打下了基础。p.21
1977年,吴文俊提出的定理机器证明新方法正式发表。使用这新方法(简称吴法),可以在微机上迅速地证明很不简单的几何定理,如西姆松定理、费尔哈定理、莫勒定理等等;还能发现新的不平凡的的几何定理。1989年,访美学者周咸青基于吴法编制的 Lisp 程序(所谓”证明器“)在计算机上证明了512条定理。这些定理大多是不平凡的,其中还有新定理。证明每条定理所用的机器时间一般才几秒钟。p.27-28
《王者之路 机器证明及其应用》吴文俊等
吴氏方法的基本思想是,先把几何问题化为代数问题,再把代数问题化为代数恒等式的检验问题。代数恒等式的检验是机械的,问题的转化过程也是机械的,整个问题也就机械化了。《数学与哲学》张景中,p.156
新闻
V & V
验证(Verification)与确认(Validation)
- Verification 验证表明的是满足规定要求。
- Validation 确认就是检查最终产品是否达到顾客使用要求。
参考
理论
形式科学是指主要研究对象为抽象形态的科学,如逻辑、数学、数理逻辑、信息论、统计学(数理统计学)、理论计算机科学(计算理论)、经济学(博弈论)等。
Metamath 是用来发展严格形式化数学定义及证明的一款语言,亦指用来验证该语言的证明验证器,以及存有逻辑、集合论、数论、群论、代数、数学分析、拓扑学、希尔伯特空间及量子逻辑等领域中数万条已证明定理且仍不断在增加中的数据库。灰狐镜像
形式逻辑有传统与现代(即数理逻辑)之分,简单地说,形式逻辑是研究思维的形式及其规律的。
数理逻辑(Mathematical logic)是数学的一个分支,其研究对象是对证明和计算这两个直观概念进行符号化以后的形式系统。数理逻辑是数学基础的一个不可缺少的组成部分。
证明论(又名元数学)是数理逻辑的一个分支,它将数学证明表达为形式化的数学客体,从而通过数学技术来简化对他们的分析。证明通常用归纳式地定义的数据结构来表达,例如链表,盒链表,或者树,它们根据逻辑系统的公理和推理规则构造。因此,证明论本质上是语法逻辑,和本质上是语义学的模型论形相反。和模型论,公理化集合论,以及递归论一起,证明论被称为数学基础的四大支柱之一。
形式(formal)语言是人工语言(constructed)的一种,是从特定的初始符号出发经过特定的形成规则所形成的语言,比如电报代码、计算机语言、数学语言、逻辑语言等。
- Formal system 形式系统 Formal language 形式语言 Formal grammar 形式文法
- satisfiability modulo theories (SMT) 可满足性模理论 SMT-COMP SMT @ Microsoft SMT-based Verification of Heap-manipulating Programs New update
- Automated theorem proving (ATP) 自动化定理证明
- First-order logic 一阶逻辑
- Theory of pure equality 纯粹的平等理论
- 形式逻辑系统
指南
在数学、逻辑和计算机科学中,形式语言(Formal language)是用精确的数学或机器可处理的公式定义的语言。
在计算机科学和数理逻辑中,证明助手或交互式定理检验器是一种软件工具,通过人机协作来协助开发形式证明。
在计算机科学和软件工程领域,形式化方法是使用适当的数学分析以提高设计的可靠性和强健性,适合于软件和硬件系统的描述、开发和验证。
形式验证(Formal verification)可以分为三大类:抽象解释(Abstract Interpretation)、形式模型检查(Formal Model Checking,也称作特性检查)和定理证明(Theory Prover)。
非形式化证明是算法,形式化证明是代码。
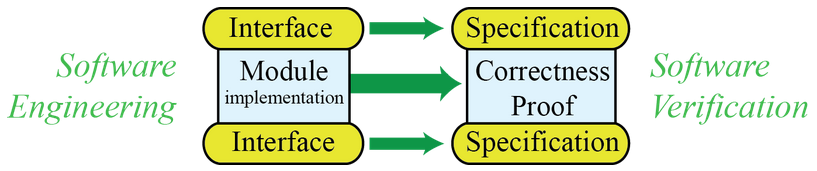 DeepSpec The Science of Deep Specification
DeepSpec The Science of Deep Specification
覆盖的核心概念有:
- 逻辑学中的基本工具,用于准确地提出并论证关于程序的假设,逻辑学被称之为计算机科学的微积分;
- 证明助理用于构造严谨的逻辑论据,分为两类:自动定理证明器和证明助理(如:Coq、Isabelle、Agda);
- 函数式编程思想,同时作为一种编程方法来简化程序的论证,以及架起程序和逻辑学之间的桥梁。
语言
- 在数学、逻辑和计算机科学中,形式语言(Formal language)是用精确的数学或机器可处理的公式定义的语言。
- F* Dafny
- Haskell Agda Idris 具有“证明即程序、命题为类型”的特征。hs-to-coq import Haskell to Coq, jukebox A theorem prover
- OCaml Coq coq-of-ocaml 可做两件事:1、do formal proofs on OCaml programs; 2、port OCaml projects to Coq.
- ML isabelle CakeML A Verified Implementation of ML
- Lisp ACL2 PVS Theorem Provers in Common Lisp
- Racket cur
- Common Lisp PRL Project Proofs as Programs
- Lean Prover
- SMT-LIB Language 包含三大组件:theory declarations, logic declarations, and scripts
- Hardware description language for Formal verification
项目
- Awesome Formal Verification

- Provably Awesome

- Proof Assistant Open Source Projects on Github
- proof assistant @ higithub
- DeepSpec The Science of Deep Specification
- Formalizing 100 Theorems
- Coq
- Agda
- Lean
- Idris
- ACL2
- Groupoid Infinity Institute is doing formalization of mathematics Made by Erlang
- Z3 Theorem Prover Programming Z3
- F* A Proof-oriented Programming Language
- CVC4
- SRI International's Computer Science Laboratory Yices SMT Solver Prototype Verification System (PVS) PVS NASALib written in Common Lisp
- hs-to-coq
- Formal Verification of Ethereum Contracts Ethereum
- HOL Interactive Theorem Prover
- HACL* a formally verified cryptographic library(形式化验证密码学库)written in F*
- Dafny is a verification-aware programming language 使用 C# 编写,采用 MIT 许可证。
- Programming with Refinement Types An Introduction to LiquidHaskell
- isabelle is a generic proof assistant Isabelle 形式化证明存档(Archive of Formal Proofs)
- The Little Prover
- Proof General Organize your proofs!
- The red* family of proof assistants
- The Principia Rewrite 《数学原理》重写工程——该项目致力于将罗素与怀特海的《数学原理》使用 Coq 语言完全重写,补全原书的逻辑漏洞,将其中的证明进行 100% 的机器形式化验证。同时,项目还会将 Coq 的证明进行排版,生成和原书风格一致、可检索、排版精致的文本供人类阅读。@Libre盖子
- Why3 是一个用于演绎程序验证(deductive program verification)的平台
- EasyCrypt Computer-Aided Cryptographic Proofs
- Frama-C using Why3
- Matita interactive theorem prover
- PRL Project Proofs as Programs
- SMT-LIB standrad Language, Theories, Logics SMT solvers such as Yices 2, Z3
- The TPTP Problem Library for Automated Theorem Proving
- Lean theorem prover Lean community Lean and its Mathematical Library
- The Kore Language K 框架符号执行引擎,Haskell 编写。
- Cardano formal verification
- HOL Light theorem prover OCaml 编写
- Vellvm Verifying the LLVM
- Kami — A Coq-based DSL for specifying and proving hardware designs
- RiscvSpecFormal Formal Specification of RISC-V ISA in Kami, written in Haskell.
- KeY Project
- TPTP (Thousands of Problems for Theorem Provers)
- GNU C-Graph Convolution Theorem Visualization(卷积定理的可视化)

STEM
- Fourth Summer School on Formal Techniques
- Iris Project Lecture Notes Iris: Higher-Order Concurrent Separation Logic
研究组织
- Yale FLINT group
- Formal Verification and Security Lab
- Programming, Logic, and Semantics Group Automated Reasoning Group
- Formal Systems Laboratory (FSL)
- Toccata Formally Verified Programs, Certified Tools and Numerical Computation
- MIT Programming Languages & Verification Group
- NASA Langley Formal Methods Research Program
- FORMAL VERIFICATION AT UTAH
- Research in Software Engineering (RiSE)
文档
- A Hybrid Formal Verification System in Coq for Ensuring the Reliability and Security of Ethereum-based Service Smart Contracts
- Isar — A language for structured proofs
- End-to-End Formal Verification of Ethereum 2.0 Deposit Smart Contract
- An Open Framework for Certified System Software Author
- Interactive Theorem Proving (ITP) Course
- Static Analysis: an Abstract Interpretation Perspective
- Modular Program Verification
- Speaking Logic
- Programming for Everyone: From Solvers to Solver-Aided Languages and Beyond
- CryptoVerif: Mechanizing Game-Based Proofs
- Interactive Theorem Proving (ITP) Course
图书
- 《Implementing Mathematics with The Nuprl Proof Development System》
- 《Mathematical Proofs: A Transition to Advanced Mathematics》 Gary Chartrand, Albert D. Polimeni, Ping Zhang
- 《Software Foundations》 软件基础系列是对可靠软件的数学基础的广泛介绍。该系列的主要创新之处在于,每一个细节都是百分之百的形式化和机器检查:每一卷的整个文本,包括练习,实际上是Coq证明助手的 "证明脚本"。
- 《软件基础》系列广泛地介绍了可靠软件的数学基础,这是《Software Foundations》中文版。
- 《Program Logics for Certified Compilers》
- 《芯片验证漫游指南:从系统理论到UVM的验证全视界》刘斌
数字集成系统的验证,是提高设计芯片一次流片成功的关键。随着芯片制造工艺的更加精细,芯片制造费用的不断增加,芯片功能越来越复杂,验证的重要性也日益增加。
- 《方程求解与机器证明 基于MMP的问题求解》 科学出版社 2008 高小山、王定康、裘宗燕、杨宏著
- 《数学机械化》 科学出版社 2006 吴文俊 著
- 《王者之路 机器证明及其应用》 吴文俊、张景中等
建立几何的代数化,使几何问题的求解转化为方程的求解。把几何问题转化为方程求得的解答,表达成几何的定理,这可视为从方程解答导致定理自动发明的某些原始实例。
图集
链接
- Runtime Verification Inc We love formal methods
- Bluespec Open Source RISC-V Cores and Tools
- Formal Land 对日常生活中的程序(everyday-life programs)进行形式化验证
- BedRock Systems Unbreakable Foundation for Formally Secured Computing, NOVA is the foundation for the BedRock HyperVisor(BHV), which combines a formally verified secure trusted computing base with VM introspection and policy enforcement.
- SiFive rapid development of custom hardware solutions, based on RISC-V, Securing The RISC‑V Revolution.
- Scalable SoC Verification 可扩展的 SoC 验证,提前启动软件系统验证
- Cadence Verification
- International Satisfiability Modulo Theories Competition (SMT-COMP) 国际可满足性模理论竞赛